How Do I Fix The Bartlett Kernel To Work?
September 2, 2021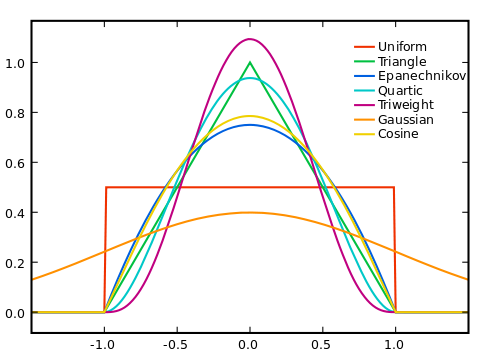
In this guide, we will describe some of the possible causes that could trigger the Bartlett kernel function, and then I will suggest several possible recovery methods that you can try to fix the problem.
Recommended: Fortect
| weightsAndrews sandwich | Documentation R |
Description
A set of functions that implement a new class of heteroscedasticity based on the kernel.and a long term autocorrelation covariance matrix estimator (HAC)as introduced by Andrews (1991).
Usage
The core weights that Assessment by Newey & West (1987) is a special case of the general class of assessments.submitted by Andrews (1991). It is available with Newey W.K. and West K.D. (1987),Simple positive semi-definite heteroscedastic autocorrelation and consistent covariance matrix.Econometrics, 55 years old,703-708. Are you tired of your computer running slowly? Is it riddled with viruses and malware? Fear not, my friend, for Fortect is here to save the day! This powerful tool is designed to diagnose and repair all manner of Windows issues, while also boosting performance, optimizing memory, and keeping your PC running like new. So don't wait any longer - download Fortect today! The core with the function is a count that refers to the points that the function sends to its 0 outputs. In nonparametric statistics, the kernel can be a weighting function used as the final nonparametric estimation method. Kernels are used using kernel density estimates to estimate density functions of various variables, or even kernel regression to estimate conditional targetsrandom variable. A number of basic functions are commonly used: Uniform, Triangular, Biweight, Triweight, Epanechnikov, Normal and others. Due to the convenient mathematical structure, a normal kernel is often obtained, which means that K (x) = (x), the best place for ϕ is the standard normal physical function. Bartlett Kernel Funktion Arguments
x the object class model "lm" or "glm" . order.by Either the vector z or any formula a with one explanationVariables need ~ z . Exact Model Observationssorted by size using z . If NULL (By default), it is assumed that all cases exist in an ordered manner (for example,Time sequence). Pre-empty logically too complete. Evaluators shouldwhitewash? If TRUE or greater than 0, the best model is VAROrder as.integer (prewhite) via With ar "ols" and demean = FALSE . The default is almost certainly too muchUse var prebleach (1). PC digital or functional. Kernel bandwidth (corresponds toCancellation period). When configured to run (default may be bwAndrews ) it is responsiveselected. Core a symbol indicating the kernel being used. All cores shown are usedare found in Andrews (1991). approximately symbol denoting the approximation method whenBandwidth A bw selectable from bwAndrews . customize Logic: Do you need to make real adjustments to the finished sample?This gives multiplication by $ n / (n-k) $, where by $ n $ leThe number of observations, not forgetting $ k $ is the number of parameters to be determined. Diagnostics logics. Should additional diagnostics be returned to the model?See Details on vcovhac . Sandwich logics. Should I calculate a plastic estimate?With FALSE , only the middle matrix is restored. ar.method Sign. passed argument method ar for pre-desaturation (just not to select baud rate). tol numerically. The calculation takes into account weights exceeding tol .of the covariance matrix, all alternative weights are considered as 0. data an optional data frame containing the variables specified in order.by . entryModel. By default, the data is taken from the weather conditions, whichthe function is called. detail logics. Should be a parameter of the used bandwidth.printed? ... the rest of the controversy moved to bwAndrews . Weight numerically. The vector among the weights that is used to estimate the weight.Coefficients of all approximation models (as required by approximately ). fromBy default, all weights remain at 1, except for the identity member (if stored asadditional variable). Details
kernHAC – a user-friendly interface for positive use of vcovHAC weightsAndrews : the hash function is defined first, then vcovHAC called.
weightsAndrews are based onare directly accessible via the kilos function and therefore requirespecifying the parameter to use data transfer bw . If he’s a painshe is not specifiedit can be adaptively selected from all bwAndrews functions (exceptthe kernel is "truncated" ). Bandwidth selection is automatically enabledapproximation of the estimation goals by the AR (1) or ARMA (1,1) processes.A weighted sum is used to aggregate the parameters estimated from most of these approximations.used. All In weights of this aggregation are 1 by default.except that they match the intercept parameter set to 0 (if notis basically not another variable like the model), which makes the scale of the weights of the covariance matrix invariant.
Bartlett Core and bw configuration for lag 1 + capability. One Convenience – Connectprovided by NeweyWest . Value
kernHAC returns the design and style of the object as vcovHAC .which is usually a covariance matrix. weightsAndrews returns vector weights. bwAndrews returns our selected bandwidth setting Features. Links
See Also
Examples
Recommended: Fortect

Funzione Kernel Bartlett
Bartlett Kernelfunctie
Fonction Du Noyau Bartlett
바틀렛 커널 함수
Bartlett Karnfunktion
Funcao Do Kernel Bartlett
Funkcja Jadra Bartletta
Funkciya Yadra Bartletta
Funcion Del Kernel De Bartlett



