CAN Bus Error Checking Solutions
September 17, 2021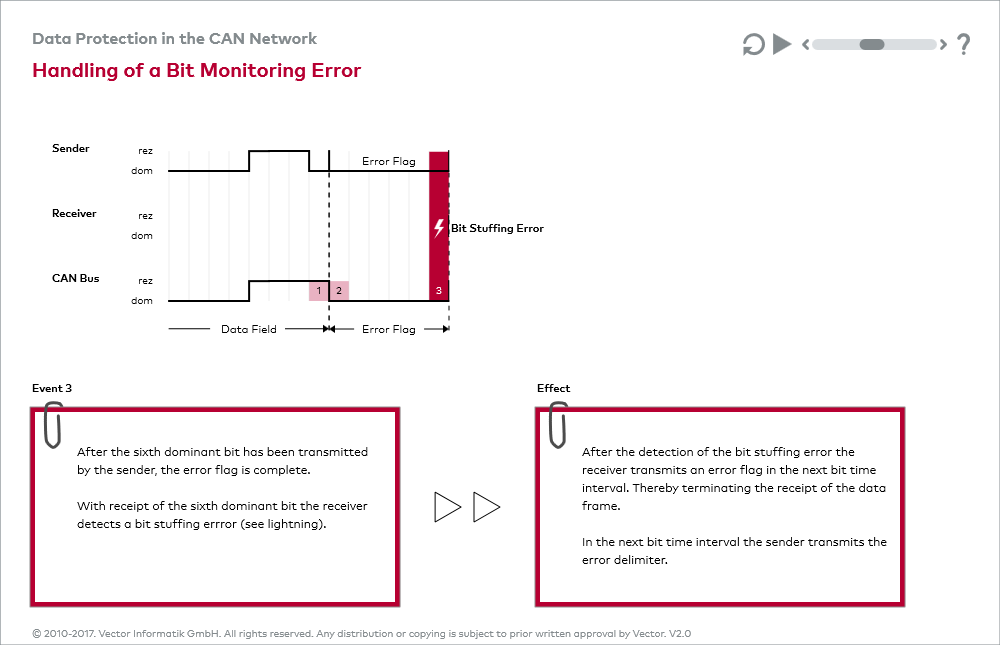
Over the past few weeks, some of our users have reported that they encountered Can-Bus errors when placing an order.
Recommended: Fortect
How Descriptors Can Fail
Error handling is currently built into the CAN protocol and has an impressive impact on performance.The length of the huge CAN system. The purpose of the error is to detect errors in petrol messages on the CAN bus so that many senders can re-transmit the wrong message. Each CAN controller connected to a different bus will try to detect errors in the message. When a fatal error is detected, the discovery node actually sends a flag, an error that corrupts bus traffic. Additional nodes simply recognize the error caused by the error flag (if those people haven’t already recognized the original error) and take appropriate action, that is, reject my current message.
Each node only stores two error counters: a transmit error counter and therefore a receive error counter. There are several rules for enlarging and / or shrinking these desktops. Optionally, the sender that detects the error will add to its transmit error counter faster than only listening nodes will increment this receive error counter. This is on the grounds that the probability is good and that the broadcaster is definitely to blame! If the error counter exceedsAs specified, each node first becomes a “passive error”, which means that the node often does not participate in the bus website at all.
By using the error counter, a functioning CAN node can not only detect errors but also localize.
Error Detection Mechanisms
Filling tips This is practiced to avoid an excessive number of DC components on the bus, but it also gives receivers an additional means of error detection: if more consecutive technical bits of the same rank appear on the bus, a padding error is reported.
Recommended: Fortect
Are you tired of your computer running slowly? Is it riddled with viruses and malware? Fear not, my friend, for Fortect is here to save the day! This powerful tool is designed to diagnose and repair all manner of Windows issues, while also boosting performance, optimizing memory, and keeping your PC running like new. So don't wait any longer - download Fortect today!

The CAN protocol defines several or at least five different capabilities, including error detection. Two of them are at the bit level and the other three are at the postman’s message.
- Bit monitoring.
- A little jam.
- Checking the frame.
- Screening exam.
- Cyclic redundancy check, monitoring
All
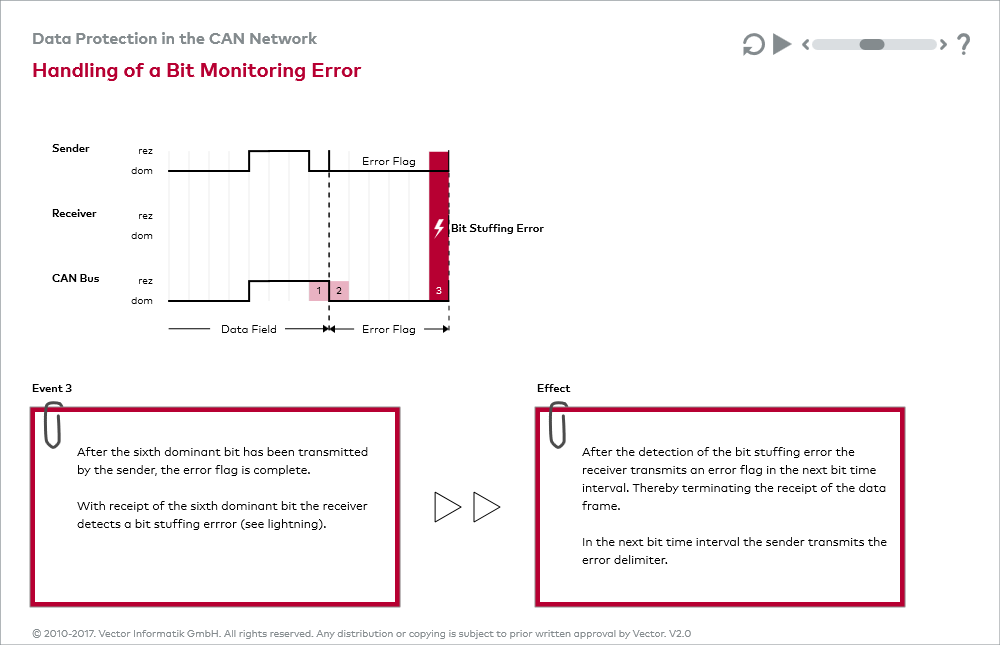
The Bit Transmitter In The CAN Stream Monitors (i.e. Reads) The Transmitted Level Signal. If The Degree Of The Actually Read Bit Differs From That Transmitted Separately, An Error Bit Is Signaled. (No Bit Errors Occur During Process Arbitration.) Bit Stuffing
When five consecutive bits of the same layer have been transmitted by a node, the node adds a sixth bit after the layer, oppositePoor to the overall bitstream. With this method, the receivers remove the extra bits. This is to avoid excessive DC components on the bus, but it also gives receivers an additional opportunity to detect errors: if more consecutive bits of the same number appear on the bus, a Stuff error message is issued. p>
Frame Check
Some parts of a CAN message have a special format i, for example, the standard specifies exactly which levels should occur, when and when. (These parts are both CRC delimiter, ACK delimiter, end of frame, and break, but there are special error checking standards for this.) If the CAN operator detects an invalid person in these fixed fields, a form error occurs. reported.
Confirmation Exam
All nodes available on the bus that correctly attract a message (regardless of whether or not they are simply “interested” in its content) can be expected to dominate the so-called justification slot at time. send a message. EmThe agent sends the recessive level here. If the sender cannot recognize the dominant zone in the ACK slot, an acknowledgment error is issued.
Cyclic Redundancy Check
Each target has a 15-bit cyclic redundancy check (CRC) checksum, and every node that mentally registers a CRC other than the one it calculated will report a CRC error.
Error Isolation Mechanisms
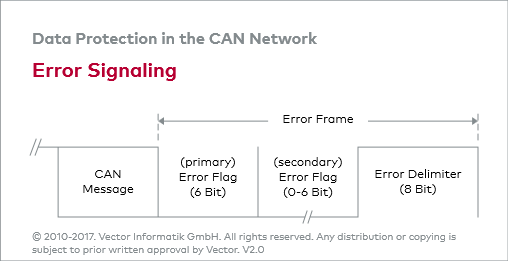
Every CAN controller on the bus will try to detect the errors described above in every message. If an error is detected, the explorer node sends a flag, the error, thereby killing the bus traffic. Other nodes recognize the error generated by the error flag (if they have not yet recognized the primary error) and take appropriate action, i.e. H. delete current message.
Each node contains two error counters: a send error counter and a receive error counter. There are several rules for increasing and / or decreasing these counters. Basically, a sender who encounters some type of error will increment their error counterto send faster than listening nodes must increment their receive error counter. This is because there is a good chance that this diffuser is to blame!
The node starts with out in active error mode. If one of the two error counters exceeds 127, node 1 goes into a state known as passive error, and if the number of transmission errors exceeds 255, the entire node goes into a bus off state.
- Active error node generates active error flags when errors are detected.
- Passive Error Node passes passive error flags when logging errors.
- A node on which Bus Off is not transmitting anything on this bus.
The rules for increasing and decreasing the counter error will certainly be a little complicated, but the general principle is simple: transmission errors give large points of failure, and reception errors give 3 points of failure. Correctly transmitted and / or messages that positively lower the counter (s).
Example (slightly simplified): Suppose the experts claim that a node on the bus is having a bad day. Every time A tries to deliver a message, it works (byfor some reason, no). Each time this point increments the send error counter by 8 and sends an active error flag. Then they experiment with forwarding the message … and the same thing happens.
If the transmitted error count exceeds 127 (i.e. 16 attempts), the node becomes passive on a minor error. The difference is that passive error flags are now transmitted over the bus. The passive error flag consists of 6 recessive bits and also does not kill other bus website visitors, so other nodes cannot hear any complaints about the mci car errors. However, I continued to increment the transmission error counter. If it exceeds 255, node A eventually yields and stops.
What are the other nodes in node A thinking? – For each valid error flag sent by A, a large number of other nodes increment their receive error counters by 1. At the very moment when A turns off the bus, other nodes have a corresponding counter in their error counters. which is well below the passive error limits, i.e. 127. This counter is decremented by one to generateRecord every correctly received message. However, the node disables the bus.
Most CAN controllers offer state tasks (and corresponding interrupts) for two states:
- Error Warning – one or both prevents errors greater than 96.
- Bus stop as above.
Some – but not all! – Remote control also provides some passive state for many errors. Some remote controls also offer direct access to error counters.
The ability of the CAN controller to automatically retransmit messages when problems occur over time can be a problem. There is at least 1 controller on the market (Philips SJA1000) that allows full manual control of jumble management.
Bus Error Modes
The widely used ISO 11898 standard lists several types of CAN bus cable failure:
- CAN_H interrupted.
- CAN_L interrupted
- CAN_H is shorted to battery voltage in the market.
- CAN_L shorted to ground
- CAN_H: short circuit to ma su
- CAN_L shorted to control voltage
- CAN_L shorted with CAN_H cable
- CAN_H and CAN_L aborted at the same point
- Lost on Line Connection
For errors 1-6 and 9, it is “recommended” that the bus survive with a much lower signal-to-noise ratio, and in the event of error 8, the creating subsystem survives. For error 7, it would “not be necessary” to survive the reduced signal-to-noise ratio. Practice
In a CAN application using 82C250 transceivers, there are no 1-7 errors, and 8-9 errors may or may not be.
Drivers, like the TJA1053, are “fault tolerant”, but sometimes they can handle all errors. Usually someone pays for this error due to the limited speed limit; that TJA1053 is one hundred twenty five kbps.
Download this software and fix your PC in minutes.
Types of CAN bus errors A CAN bit error occurs if the monitored value deviates from the sent value. For example, if a node is dominant (0) for a bus, but is determined to be recessive (1), this is likely to cause a bit error. A small error can also be identified as being stuck.
If they match, the frame is considered to be received correctly, and the take profit node sends a dominant state, usually in the ACK slot bit, overriding the specific recessive state of the sender. In the event of a mismatch, the affected node sends an error frame after the ACK delimiter.
Kann Busfehlerprufung
Puo Controllare Gli Errori Del Bus
Kan Bus Foutcontrole
Verification Des Erreurs De Bus
버스 오류 검사
Pode Barrar Verificacao De Erros
Kan Bussfelskontroll
Proverka Oshibok Shiny Can
Puede La Comprobacion De Errores Del Bus
Czy Sprawdzanie Bledow Magistrali





