Footnote Unknown Capi Error? Repair Immediately
December 27, 2021
Recommended: Fortect
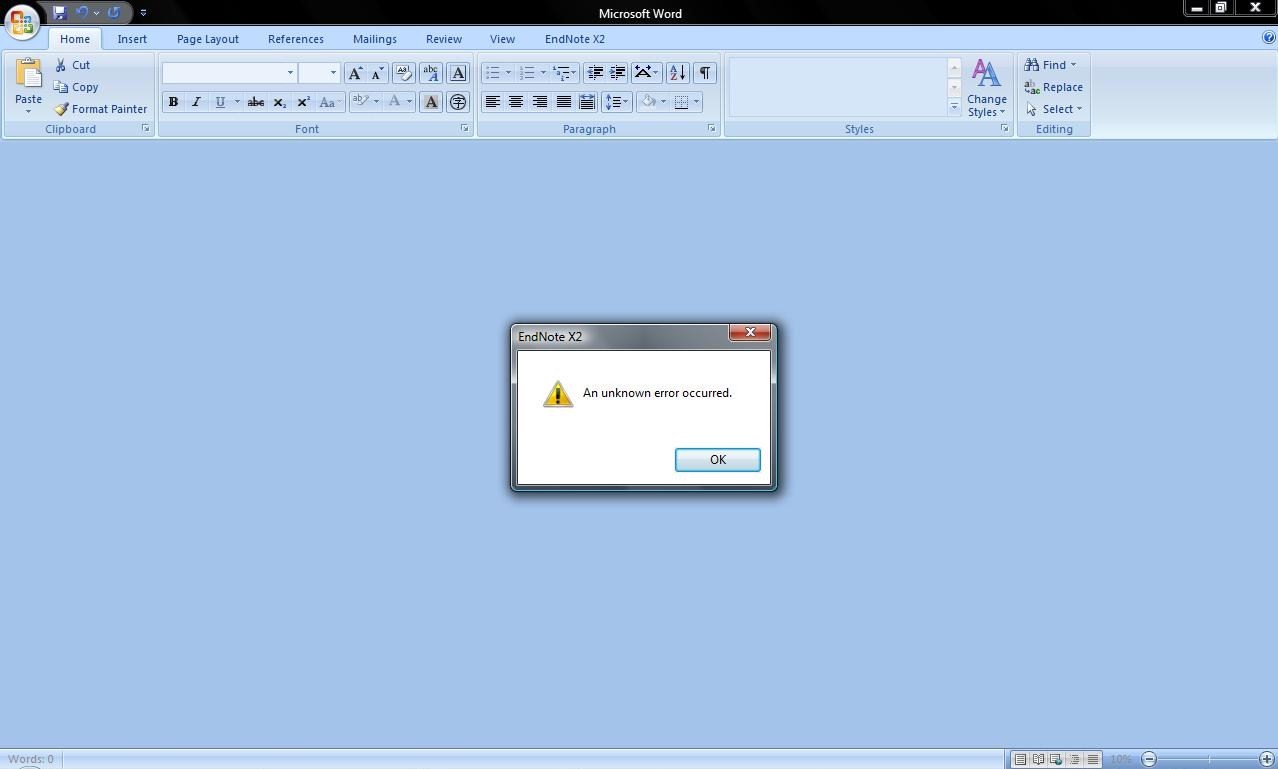
Hope that if there is an unknown Capi error on your system, this article can help you fix it.
- up
- JRM
- paper
- Robot003000060873
single-rb.php
JRM – Vol.30 No. 6 –S.873-879
In Word, click any File tab and select Options. Select add-ons in the left pane. Under the heading Active Application Add-ins, make sure you have the EndNote Cite While You Write COM add-in (see Type column). If it’s not listed, go to the bottom of the Manage drop-down window.
doi: 10.20965 / jrm.2018.p0873
D. Mac OS Mojave and later also include new security and privacy features that may interfere with the correct automation of EndNote. Make sure Microsoft Word and EndNote X # are enabled. If this automation is disabled, the Cite While You Write functions should definitely not work.
(2018)
Paper:
Additional calls compared to the last 60 days:1330
Chao Shao * , Junki Togashi ** , Mitobe * , Kazuhisa And Genchi Kapi ***
* Department of Mechanical Engineering, Yamagata University, 4-3-16 Yonezawa, Yamagata 992-8510, Japan
** Kumagaigumi Co., Ltd. de 1043 Onigakubo, Tsukuba 300-2651, Japan
*** Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Hosei University, 3-7-2 Kazinocho, Koganei, Tokyo 184-8584, Japan
The first thing you should try is, for example, close Word and EndNote in conjunction with restarting your Macintosh. Open this document and EndNote and try using the tools again. We realized that in many cases this will definitely fix bugs.COM.
Open your EndNote collection and Word document.Select the methodically ordered quote you want to edit.On the Word EndNote ribbon, click Edit Quote (s). Alternatively, you can right-click and select Change Rates.
Winding drums for robots with elastic bands
This article is about positioning control – an elastic robotic arm that controlsmy sinews like gravity. The robot is powered by elastic cables and packing drums are attached to the outside of the frames. The rubber ropes available in the industry are used as bundles. The advantage is to take advantage of the non-linear nature of rubber materials to obtain an inexpensive and flexible adjustable rate mortgage. In theory, intense gravity compensation requires a mathematical model with reliable parameters and accurate measurement of the weight of your payload. However, the need to take into account detailed information about the robot makes it difficult for its versatility, adaptability, as well as cost effectiveness. This article presents methods for re-evaluating and compensating for a new payload based on the stationary operating position error and the nominal tightening factor. Due to the non-linearity of real rubber cables, the operating error persists after one operation in combination with gravity compensation. However, experience shows that a simple repetition of the same paymentyou labor will reduce the error. Taking into account the nonlinearity of silicone strings, the mechanism is analyzed theoretically unambiguously, which reduces the number of errors. While the exact iterative process takes time, some methods require less information in advance. In addition, it is inexpensive as more than a sophisticated force sensor is required. Since the mechanism is applicable to typical rubber wire materials due to fewer errors, it makes sense to work with substantial, reconfigurable robots to keep costs down.
- [1] Yu Xu and RP Paul, “Robot Wrist Compatible System for Vehicle Assembly,” IEEE Int. Robotics and Flight Automation Conference, .3, pp. 1750-1755, 1990.
- [2] K. Koganezawa, H. Inomata, and T. Nakazawa, “A Drive with an Elastic Nonlinear Computer SystemMoy and its application on the wrist with 3 degrees of freedom ”, Int. Conf. About mechatronics and industrial automation, 3, p. 1253-1260, 2005
- [3] N. Saga, J. Nagase and Y. Kondo, Development of a motorized muscular system using a pneumatic balloon, J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol. 18, No. 2, pp. 139-145, 2006.
- [4] M.T. Mason, “Matching and Force Control Computers for Controlled Manipulators,” IEEE Trans. by Systems, Man also Vol. cybernetics, 11, issue 6, pp. 418-432, 1981.
- [5] B.J. Weibel and H. Kazerooni, “Robot Theory and Experiments for Accurate Stability of Compliance Control,” IEEE Trans. on robotics and industrial automation, 7, No. 1, pp. 95-104, 1991.
- [6] M. H. Reibert and J. J. Craig, “Hybrid Position / Force Control of Manipulators,” ASME J. von Dynamic Systems, Measurement, Control, and then Vol. 103, No. 2, pp. 126- 133, 1981.
- [7] GK Klute, JM Chernieki, not to mention B. Hannaford, McKibben’s Artificial Pneumatic Muscle Power: Actuators with Biomechanical Intelligence, Proc. Int. Conf. About the advanced intelligent mechatronics PP. 221-226, 1999.
- [8] B. Tondu and P. Lopez Modeling and Controlodes of robots with artificial McKibben muscles “, IEEE Control Systems Journal, pp. 15–38, 2000
- [9] T. Noritsugu, M. Kubota, and S. Yoshimatsu, Development of a Flexible Silicone Rubber Pneumatic Slewing Actuator, J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol. 13, No. 1, p. 17-22, 2001
- [10] G. Tonietti, R. Schiavi and A. Bicchi, “Design and Control of Variable Rigidity Drive for Safe and Fast Physical Human-Robot Interaction,” Int. Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 526-531, 2005.
- [11] K. Koganezawa, Yu. Watanabe and N. Shimizu, “Antagonistic Muscle Drive, Its Application and Multi-d.o.f. Advanced Forearm Prosthesis “, Robotics, Volume 12, No. 7-8, pp. 771-789, 1997.
- [12] G. A. Pratt and M. M. Williamson Series, Adaptation Mechanisms, Int. Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Volume 1, pp. 399-406, 1995.
- [13] N. Hogan, “Impedance Management: A Manipulation Approach: Part II – Implementation,” ASME, J. Dyn. Sys. Dimensional control, volume 107, no. 1, pp. 8-16, 1985
- [14] T. Tsuji, “The human hand in the impedance of multi-joint movements,” P.G. Morasso and V. Sanguineti (ed.), “Self-Organization, ComputeNny cards and, as a result, “control”, motor Elsevier, p. 357-380, 1997.
- [15] J. Togahsi, K. Mitobe and G. Kapi, “Controlling an Adaptable and Low-Cost Robotic Arm Powered by Elastic Tendons,” J. Robot. Mechatron., Vol. 28, No. 4, pp. 509-522, 2016.
- [16] T. Lens and O. von Strick, “Investigation of the Safety of Human-Robot Interaction for a Sequentially Resilient Tendon-Driven Robotic Arm,” Int. Conf. Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pp. 4309-4314, 2012.
- [17] T. Lens and O. von Strick, “Structural Dynamics and Model of Another Lightweight Robot Arm with Resilient Tendon Drive,” IEEE Int. Conference on Robotics in Automation (ICRA), Karlsruhe, pp. 4512-4518, 6.-10. May 2013
- [18] H. Kobayashi, K. Hyoudou, and D. Concerning ogane, robotic tendon mechanisms with redundant tendons, Int. Journal of Robotics Research, Vol. 17, No. 5, p. 561-571, 1998.
- [19] H. Aschemann and D. Schindele, “Comparison of Human Approaches to Compensating the Hysteresis of General Strength Characteristics of Pneumatic Muscles,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., V. 61, pp. 3620-3629, 2014.
- [20] CJ Lin, CR Lin,SK Yu and CT Chen, “Modeling and Controlling Hysteresis of the Double Pneumatic Pseudomuscle of Prandtl-Ishlinsky Using the Model,” Mechatronics, Vol. 28, pp. 35–45, 2015
- [21] SL Xie, HT Liu, JP Mei and GY Gu, “Modeling and Compensating Asymmetric Hysteresis as Pneumatic Artificial Muscles Using a Modified General Prandtl-Ishlinsky Model”, Mechatronics, vol. 52, pp. 49-57, 2018
- [22] S. Song, SK Xie, Z. Zhou, and Yu Hu, “Modeling an absolute pneumatic artificial muscle using a hybrid artificial neural network of computers,” Mechatronics, Vol. 31, pp. 124-131, Jan 2015
- [23] S. Arimoto, “Nonlinear Control Theory of Mechanical Systems: An Approach Based on Passivity and Circuit Theory,” Clarendon Press Oxford, pp. 174-176, 1996.
- [24] R.M. Murray, Z. Lee, in addition to S. Sastri, A Mathematical Introduction to Robot Manipulation, CRC Press, 1994. Website
Recommended: Fortect
Are you tired of your computer running slowly? Is it riddled with viruses and malware? Fear not, my friend, for Fortect is here to save the day! This powerful tool is designed to diagnose and repair all manner of Windows issues, while also boosting performance, optimizing memory, and keeping your PC running like new. So don't wait any longer - download Fortect today!

* It is simply designed with HTML5 plus CSS3 for modern browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Opera Edge ,.
Download this software and fix your PC in minutes.Onbekende Capi Fout Eindnoot
Nota Di Chiusura Errore Capi Sconosciuto
Nota Final De Error De Capi Desconocido
Okant Capi Fel Slutnot
Note De Fin D Erreur Capi Inconnue
Primechanie K Neizvestnoj Oshibke Capi
Nota Final De Erro Capi Desconhecido
알 수 없는 대문자 오류 미주
Unbekannter Capi Fehler Endnote
Nieznany Przypis Koncowy Bledu Capi